Australians call them “runners,” the British know them as “trainers,” and Americans refer to them as “tennis shoes” or “sneakers.” No matter what name you use, these rubber-soled, casual shoes are loved by billions worldwide. First appearing in the late 19th century, sneakers have come a long way since their simple canvas and rubber beginnings. Today, sneaker consumption is off the charts, especially in the United States where people buy an average of three pairs a year.
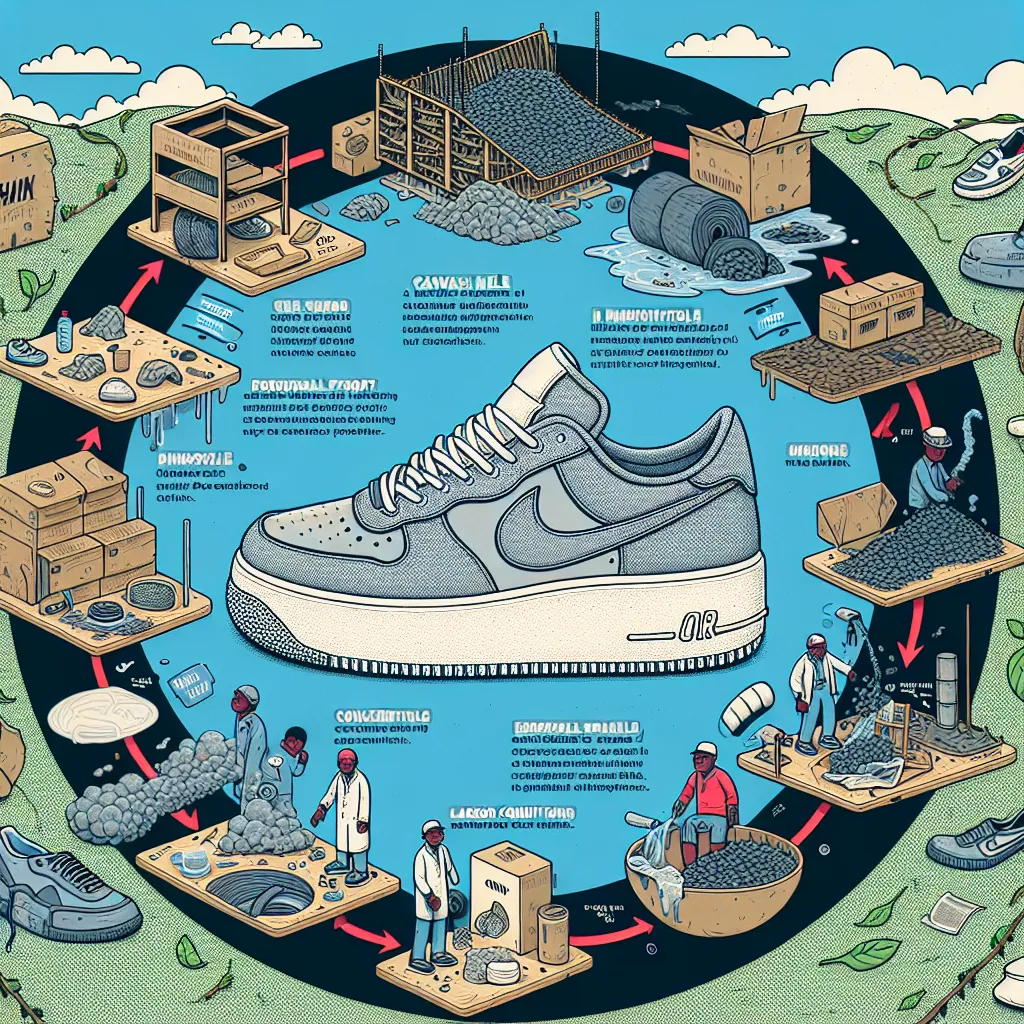
To meet this huge demand, around 23 billion shoes are made each year, mostly in factories across China and Southeast Asia. However, making shoes has grown increasingly complex, labor-intensive, and harmful to both workers and the environment. Sneaker manufacturing is responsible for about one-fifth of the fashion industry’s carbon emissions. In fact, sneakers alone produce 313 million metric tons of carbon dioxide each year, equivalent to the annual emissions of 66 million cars.
To better understand this, let’s break down what makes a sneaker. Key parts like the heel, insole, midsole, and upper layer are typically made from synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, latex, and polyurethane. Extracting the fossil fuels for these materials produces tons of greenhouse gases. Plus, transforming these raw ingredients into synthetic textiles uses a lot of energy, further adding to pollution. Some sneaker tops are made from leather, but tanning leather involves chromium—a harmful chemical that can damage freshwater ecosystems.
The outer soles are usually made of rubber that has undergone vulcanization, a process which adds sulfur to superheated raw rubber, creating a sturdy yet elastic material. While natural rubber was once used, most shoe soles today are made from a synthetic blend of natural rubber and oil byproducts, which account for 20% of a sneaker’s carbon footprint.
Much of a shoe’s environmental impact, more than two-thirds, comes from manufacturing. A standard sneaker has about 65 parts, each crafted by specialized machinery in different factories. Transporting these parts to a central assembly plant adds even more CO2 emissions. Once there, these components go through numerous steps like cutting, pouring, melting, baking, cooling, and gluing before finally being stitched together. The assembly line process involves over 360 steps, contributing another 20% to a sneaker’s environmental footprint.
This scattered manufacturing also leads to labor issues. Brands typically don’t own these factories, which are located in countries with weak labor laws. As a result, many workers earn below a living wage and are exposed to harmful chemicals like toxic glue fumes. Once manufactured, shoes are packaged and shipped worldwide. While a good pair could last years, frequent runners might need replacements every six months.
Because sneakers are made from so many materials, they’re difficult to recycle. About 20% are incinerated, while the rest end up in landfills, taking up to 1,000 years to decompose. So, how do we balance our love for sneakers with sustainability?
Designers should simplify sneaker designs and use eco-friendly materials. Factories need to develop energy-efficient processes that streamline production. Consumers can help by supporting companies that use clean energy and ethical labor practices. We can also buy fewer shoes, wear them longer, and donate those we don’t need.
No matter your style, we can all take steps toward a more sustainable future.